Which PPE Can be Used to Work with in Composite Manufacturing?
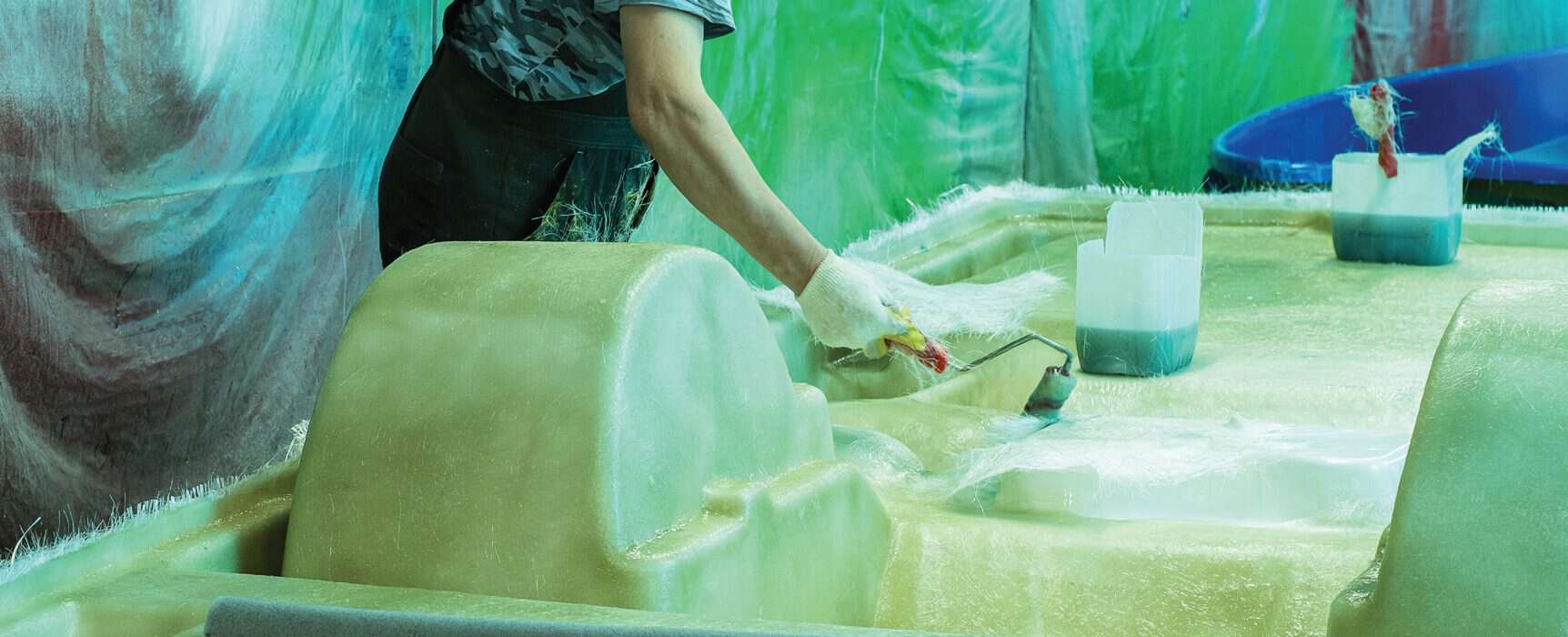
Composite materials, composed of two or more distinct elements, are becoming increasingly popular in industries that manufacture composites, thanks to their unique features and benefits. In this document, we provide an overview of composite manufacturing. This starts with defining what composite materials are and extends to their varied uses.
Here we will also discuss the composite manufacturing process in detail, which includes important stages such as layup, curing, and finishing. Additionally, identifying the potential risks associated with composite manufacturing, such as exposure to dust, chemicals, and noise, is crucial. By acknowledging and mitigating these hazards, manufacturers can create a safer work environment using appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
Composite materials – a definition
Composite materials are blends of different substances, such as fibres and resins, combined to create a single, stronger substance. These compounds often outperform individual components, used extensively in industries such as aerospace, automotive, construction, electronics, and marine, etc.,
How composite materials are made
Making composites means combining different materials to get something better. Here is how the process normally proceeds:
- Select materials – choose the primary and reinforcing components based on desired characteristics
- Prepare reinforcements – cut reinforcing materials to the required length
- Combine components – mix the primary material with the reinforcements
- Arrange layers – stack the combined materials according to the design specifications
- Cure and bond – apply heat or pressure to secure the materials together
- Trim and shape – remove excess material and refine the product’s appearance
- Quality control – conduct tests to ensure the product meets set standards
- Additional procedures – apply finishing touches such as painting if needed
- Final inspection – confirm the product adheres to quality specifications before dispatch
- Distribution – package the finished product and send it to its intended destination
Potential hazards and risks
In the field of composite manufacturing, a variety of hazards can be effectively addressed using Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). The following outlines the types of hazards and the corresponding protective measures:
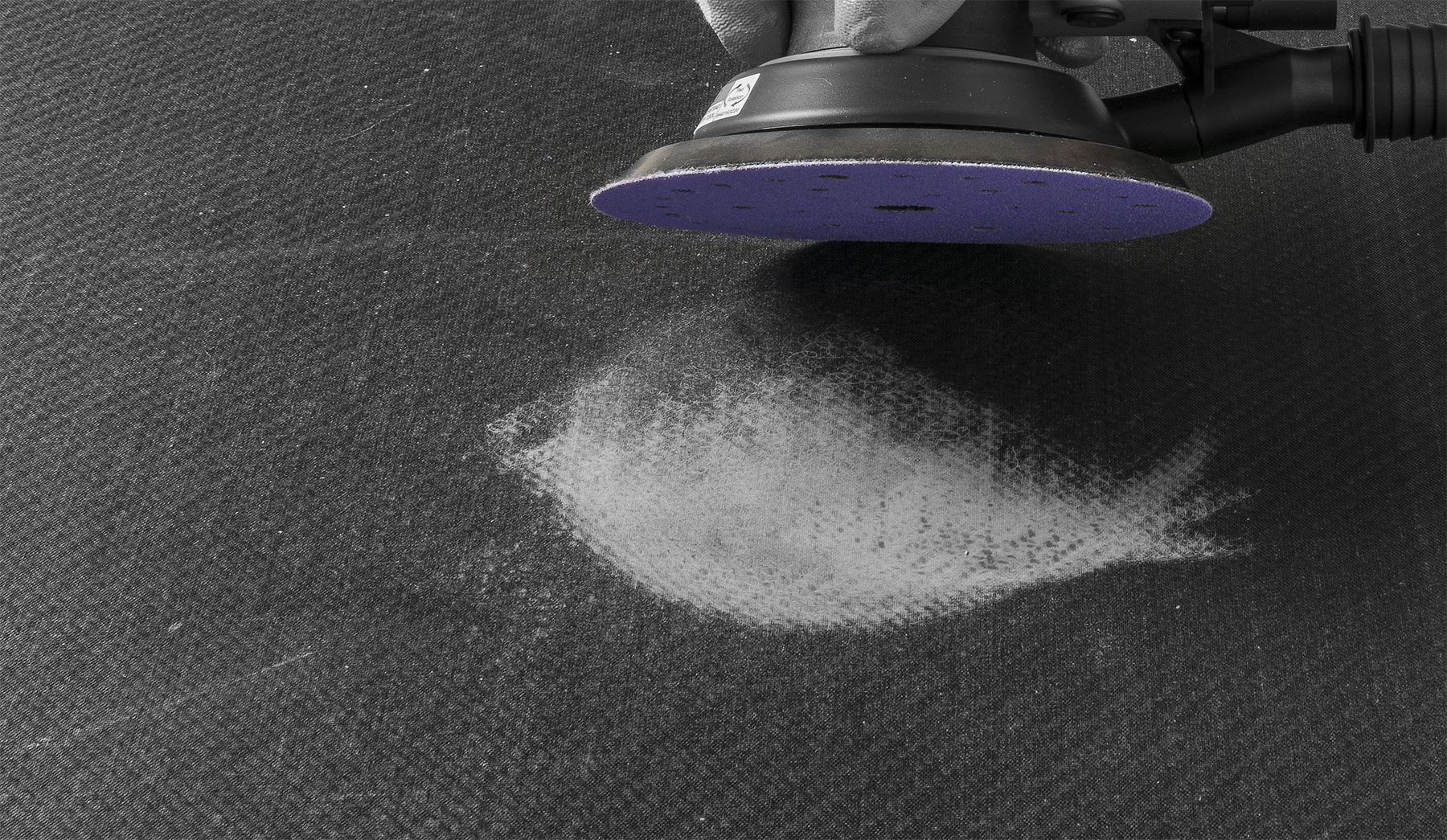
Exposure to dust
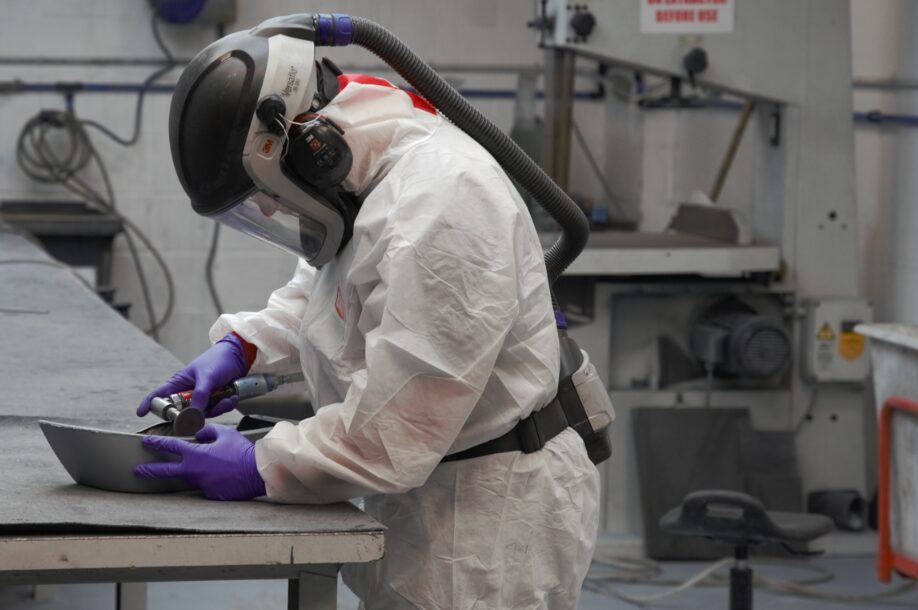
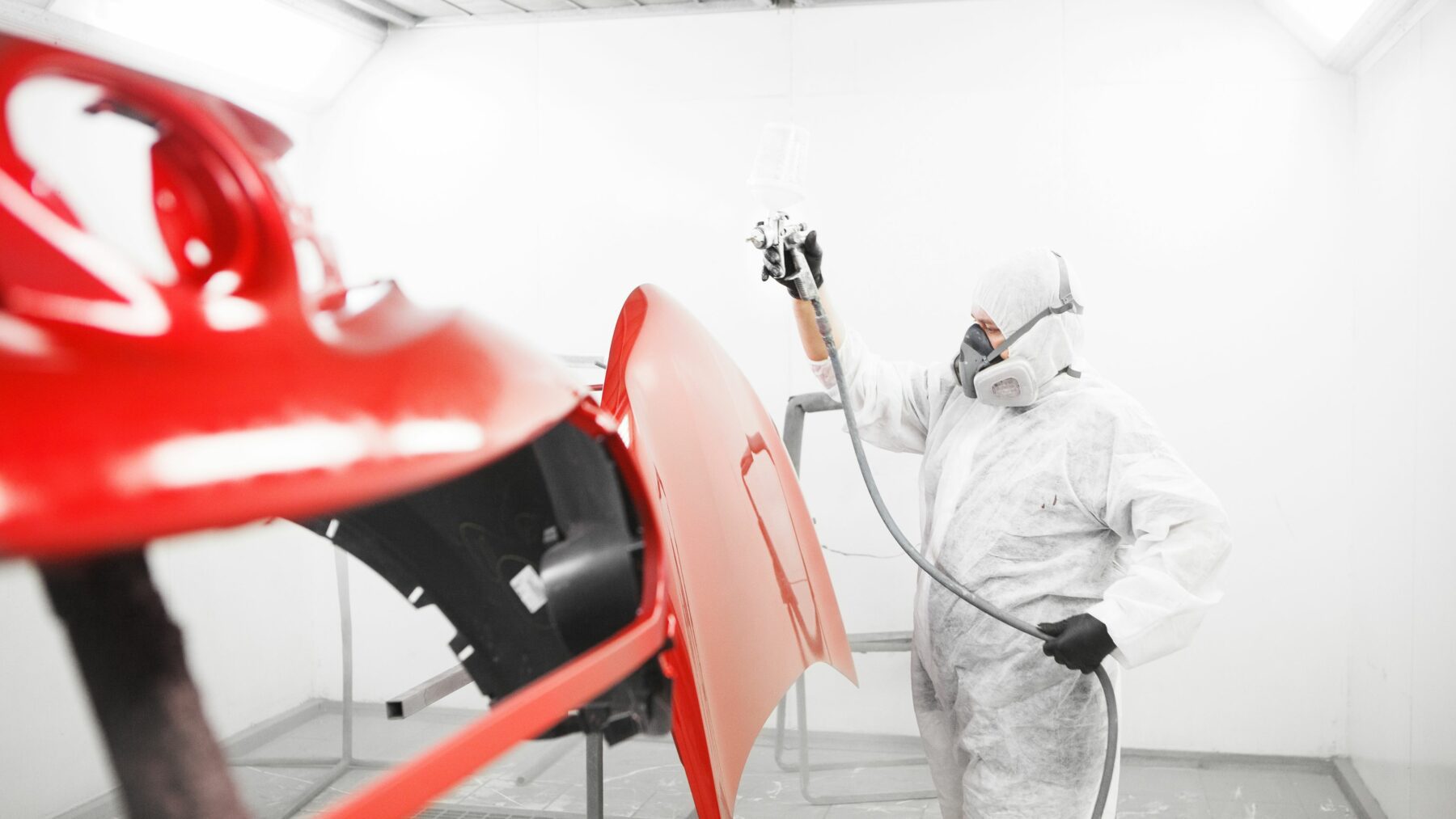
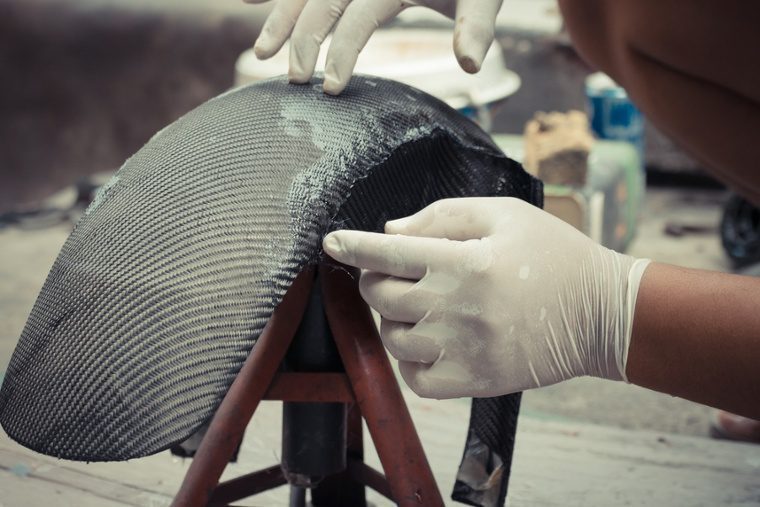
Utilising composite PPE such as dust masks or respirators is a proven method to protect employees from inhaling particles that become airborne during operations like sanding, cutting, or grinding of composite materials.

Equipment such as this full face respirator and mask are ideal for dust protection
Chemical contact
The use of chemical-resistant gloves, aprons, and face protection or eye protection such as goggles, or face shields is recommended to protect workers from direct contact with chemicals integral to the composite manufacturing process. These chemicals may include, as examples, resins, solvents, and adhesives.
Skin and eye irritation
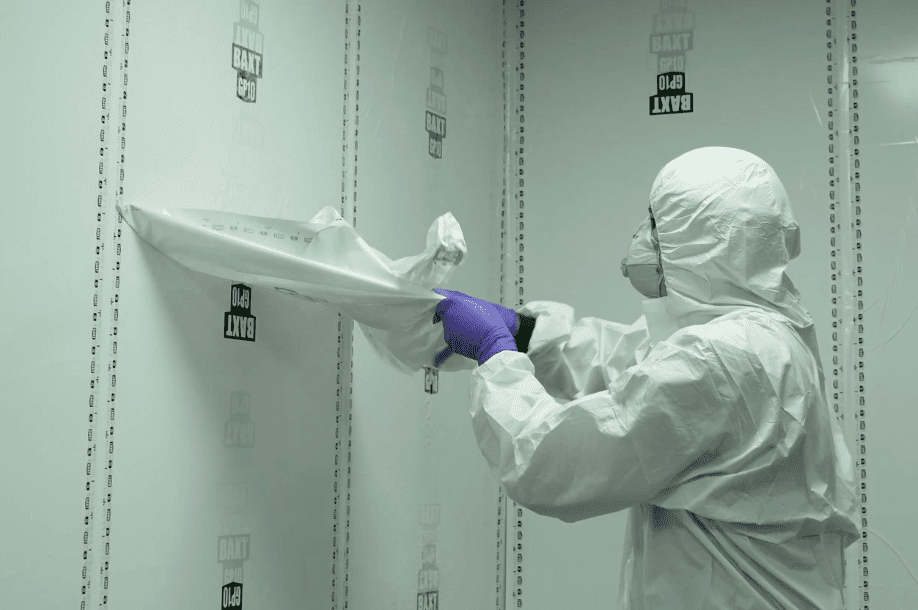
Employing safety eyewear, face shields, and comprehensive body suits is advised to defend against skin and eye irritation that may arise from handling composite materials or associated chemicals.
Noise
Earplugs or earmuffs are useful in safeguarding workers from high levels of noise produced by various machines and equipment in the composite manufacturing process. This type of hearing protection is especially important in environments where prolonged exposure to loud noise is common, as it helps to prevent potential hearing damage or loss.

Earplugs are invaluable at protecting hearing loss in composite manufacturing
Heat and flames
Flame-resistant clothing and face shields may be necessary when working with heated moulds or curing processes involving raised temperatures. This protective gear is essential for reducing the risk of burns and other heat-related injuries.
Falling objects
Hard hats or helmets serve as crucial protective gear for workers, shielding them from potential head injuries that can be inflicted by falling tools, materials, or other overhead hazards. These safety items are particularly important in environments where there is a risk of objects falling from height, or where workers might accidentally bump their heads against fixed structures.
Sharp objects
Cut-resistant gloves are essential for safeguarding workers’ hands from potential injuries when dealing with sharp composite materials or tools. These specialised gloves are often made from materials that resist tearing and puncturing, providing an additional layer of security during operations that involve cutting, slicing, or handling pointed objects.
Electrical hazards
Insulating gloves and safety footwear are critical for shielding workers from electrical risks in settings where electrical equipment is utilised. These forms of personal protective equipment are specifically designed to offer high levels of electrical insulation, thus helping to prevent electrical shocks or electrocution incidents in the workplace.

Protect workers from electrical hazards with these wellington boots
Slip and fall risks
Slip-resistant footwear is essential for minimising the risk of falls on potentially slippery surfaces found within composite manufacturing settings. By providing enhanced grip and stability, such footwear contributes significantly to the overall safety of employees, particularly when they are navigating wet or oily floors.
Heavy lifting
Back support belts and ergonomic lifting techniques can help reduce the risk of back injuries when handling heavy composite materials or components.
Exposure to UV radiation
Protective clothing, such as UV-resistant suits and face shields, can mitigate the risk of skin and eye damage caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation during curing processes.
Resin splash
Face shields or goggles equipped with splash guards are crucial for defending against accidental splashes of resin or other hazardous liquids in the composite manufacturing process. These protective measures are especially vital when workers are handling or mixing volatile substances, as they help prevent eye or facial injuries that could result from unforeseen splashes or spills.
Vibration
Anti-vibration gloves may be used to reduce the effects of hand-arm vibration syndrome when operating vibrating tools or equipment.
Importance of PPE training
Proper training on the correct use of composite PPE and adherence to safety protocols are essential for ensuring the effectiveness of these protective measures in the composite manufacturing industry.
Recommended composite PPE
| PPE category | Recommended products |
| Ears and Hearing | Earplugs and earmuffs |
| Eyes and Face | Safety goggles, face shields, or protective eyewear |
| Feet and lower legs | Safety boots and slip-resistant footwear |
| Hands and skin | Nitrile gloves, coveralls, or aprons |
| Lungs and airways | N95 respirators, PAPRs, or powered air-purifying masks |
In summary
To sum up, composite materials provide distinct benefits and have a wide range of applications across multiple sectors. This report has broken down the complex procedure of manufacturing composites, from picking the raw materials to the delivery of the finished product. We have also emphasised the different safety concerns tied to the manufacturing activity, like exposure to chemicals and breathing in dust. The significance of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) in reducing these hazards cannot be overstated, and thorough training in how to use this equipment effectively is imperative for a secure workplace.
Contacting DTC
DTC are always here to assist you with your enquiries about composite manufacturing products and the provision of composite PPE. If you need any further information, please contact us in any of the following ways:
- Contact information – https://www.dtc-uk.com/contact
- Phone us – 023 8025 1100, or by
- Send emails – sales@www.dtc-uk.com