The Role of Fillers in the Composite Industry

This article looks at the role fillers play in the composite industry, it discusses the general understanding of how they work and how their properties demand they should be taken more seriously.
In the rapidly evolving world of composite materials, fillers are the unsung heroes driving innovation and enhancing performance. These materials, often overlooked in favour of more glamorous components, play a crucial role in defining the properties and applications of composite products. As the composite and paint markets continue to expand, understanding the significance and potential of fillers becomes imperative for professionals seeking to stay ahead of the curve
Understanding Fillers
Fillers are materials added to a composite matrix to modify its properties, improve performance, or reduce cost. They can be organic or inorganic, and their selection depends on the desired characteristics of the final product. Common fillers include minerals like calcium carbonate, talc, and silica, as well as synthetic options such as glass beads and carbon black.
These additives are not merely "fillers" in the traditional sense. They are critical in enhancing mechanical properties, thermal stability, and durability of composites. By carefully selecting and incorporating fillers, manufacturers can tailor composites to meet specific requirements, making them suitable for various applications from aerospace to automotive, and even consumer goods.
Enhancing Mechanical Properties
One of the primary functions of fillers in composites is to enhance mechanical properties. For instance, adding carbon black or silica can significantly improve a composite material's tensile strength and stiffness. This is particularly important in applications where high performance and reliability are paramount, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries.
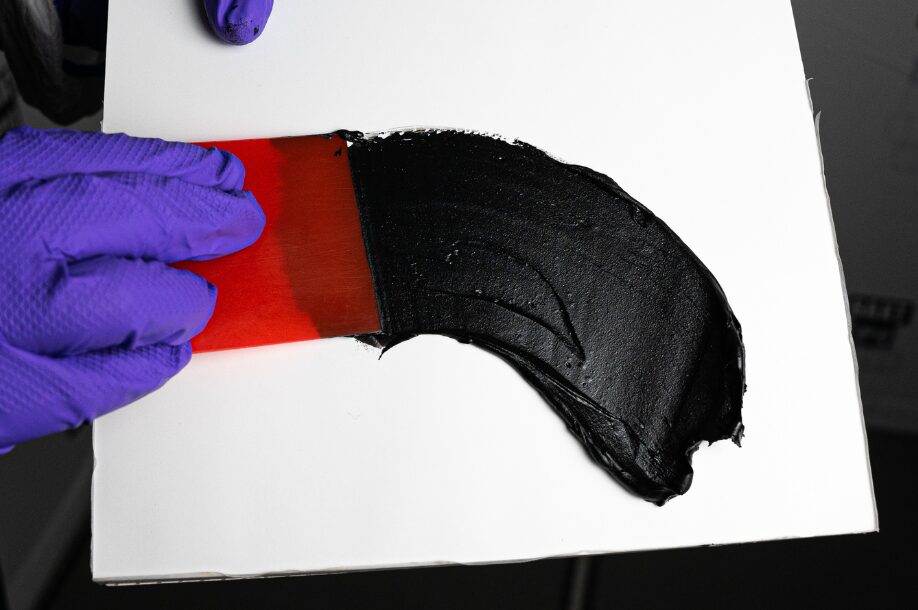

Moreover, fillers like glass beads and ceramic particles are used to improve the wear resistance and impact strength of composites. This makes them ideal for components subjected to harsh operating conditions, extending the lifespan and reliability of the products.
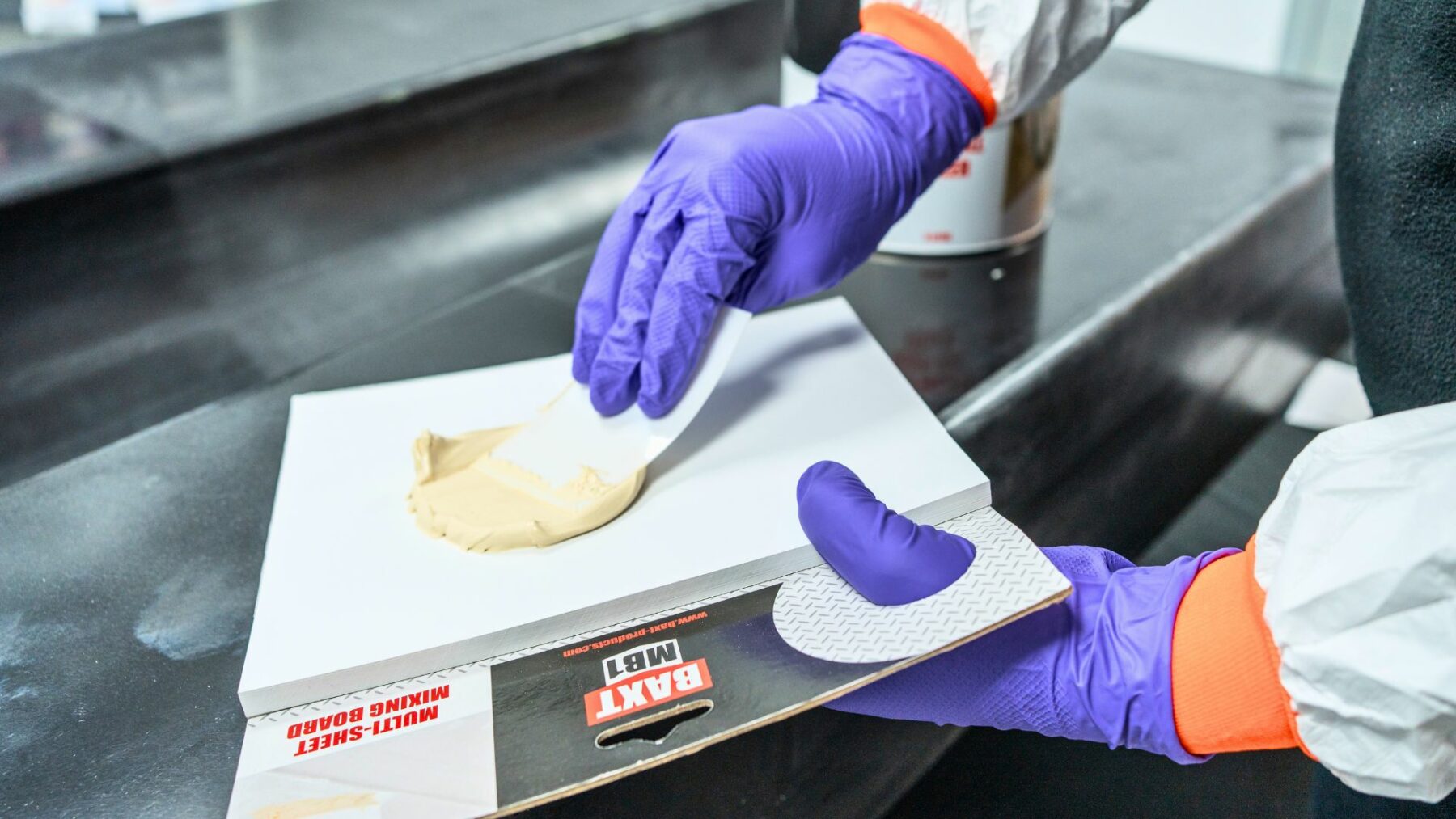
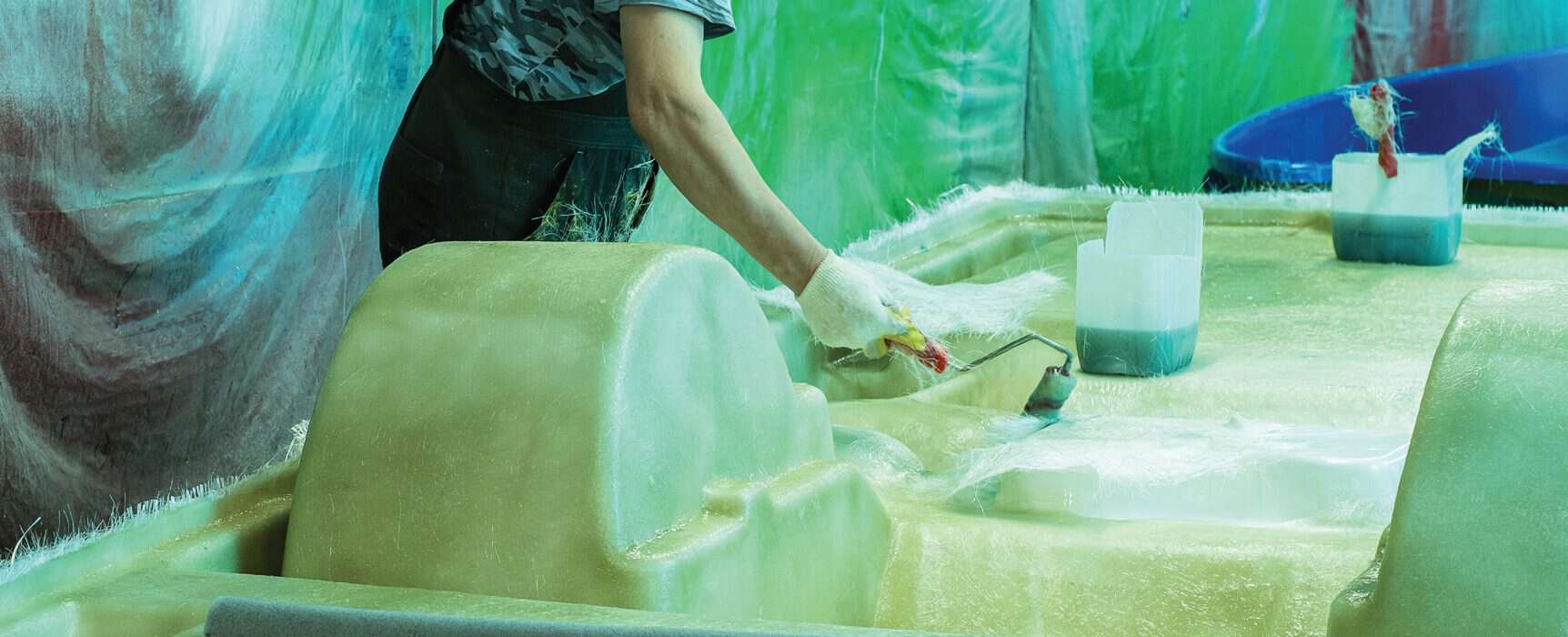
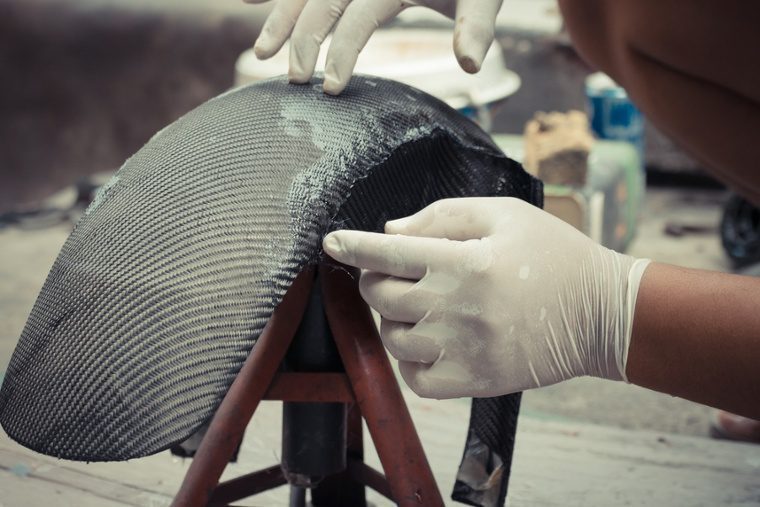
(Product in image is BAXT CARBONfil Black Polyester Filler)
Click HERE to view
Thermal Stability and Conductivity
In applications where thermal stability is crucial, fillers play an indispensable role. For example, boron nitride and aluminium oxide are commonly used to enhance the thermal conductivity of composites, which is essential for electronic and electrical applications. These fillers help dissipate heat, thereby preventing overheating and ensuring the longevity of the components.
On the other hand, fillers like mica and talc improve the thermal stability of composites, making them suitable for high-temperature environments. This property is particularly beneficial in the automotive industry, where components are often exposed to extreme temperatures.
Cost Efficiency and Weight Reduction
Fillers also contribute to the cost efficiency and weight reduction of composite materials. By replacing a portion of the more expensive resin matrix with fillers, manufacturers can reduce the overall material cost without compromising on performance. This is particularly advantageous in the production of large-scale components where cost savings can be substantial.
Additionally, lightweight fillers such as hollow glass microspheres and certain polymeric fillers are used to reduce the density of composites. This results in lightweight materials that are highly desirable in industries like aerospace and automotive, where reducing weight can lead to significant fuel savings and improved performance.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Appeal
In the paint and coatings industry, fillers play a vital role in enhancing the surface finish and aesthetic appeal of products. Fillers like calcium carbonate and talc improve the opacity and whiteness of paints, resulting in a smoother and more attractive finish. Furthermore, these fillers can improve the rheological properties of paints, making them easier to apply and ensuring a more uniform coverage.
Innovations and Future Trends
The field of fillers in composites is witnessing continuous innovation, driven by the need for materials with superior properties and sustainability. Recent research into this explores the development of novel fillers derived from renewable sources and industrial by-products. These eco-friendly fillers not only enhance the properties of composites but also address environmental concerns, making them an attractive option for the future.
Nanotechnology is also playing a pivotal role in the evolution of fillers. Nanofillers, such as carbon nanotubes and graphene, offer exceptional mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties, opening new possibilities for advanced composite materials. These nanofillers are set to revolutionise various industries by enabling the production of composites with unprecedented performance characteristics.

Summary
Fillers are integral to the advancement of composite materials, offering a myriad of benefits that enhance performance, reduce costs, and enable new applications. As the composite and paint markets continue to grow, staying informed about the latest developments in filler technology is crucial for professionals aiming to drive innovation and maintain a competitive edge.
By embracing the potential of fillers, we can push the boundaries of what composite materials can achieve, paving the way for a future where composites are stronger, lighter, and more versatile than ever before. The journey of fillers from mere additives to vital components is a testament to the relentless pursuit of excellence in the composite industry.